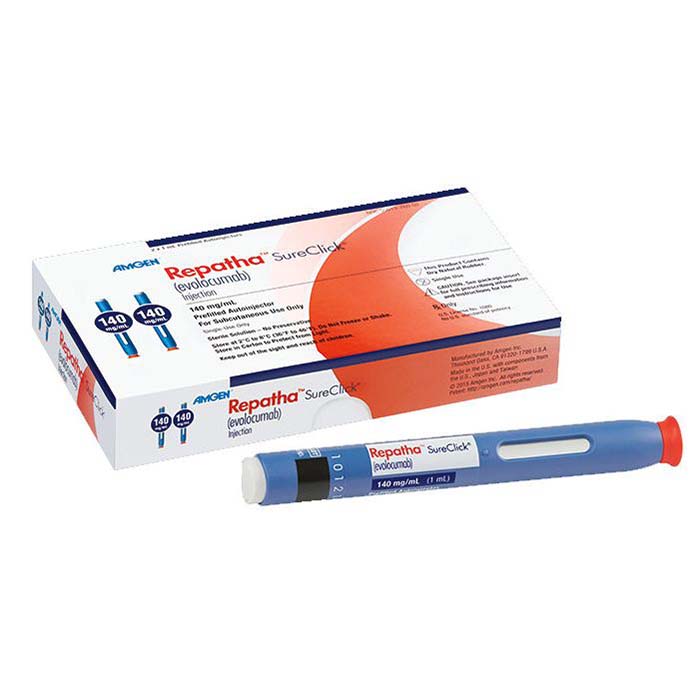
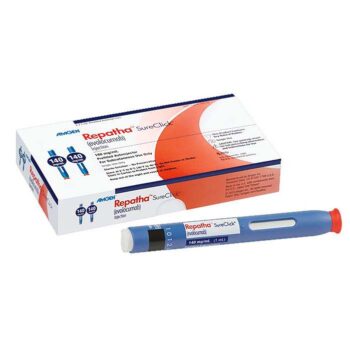
Repatha (evolocumab) is a prescription medication used to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in adults with primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia and in individuals with clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional LDL cholesterol reduction. Repatha is a subcutaneous injection that can be self-administered by patients or by a healthcare provider.
Uses:
Repatha is used to lower LDL cholesterol levels in adults with primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia and in individuals with clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional LDL cholesterol reduction.
Storage Conditions:
Repatha should be stored in the refrigerator between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C). Prior to administration, the medication should be allowed to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes.
Mechanism of Action:
Repatha is a type of monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9). PCSK9 is a protein that degrades LDL receptors, reducing the clearance of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. By inhibiting PCSK9, Repatha increases the number of LDL receptors on the surface of liver cells and other cells, promoting the clearance of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
HOW TO USE:
Repatha is a subcutaneous injection that can be self-administered by patients or by a healthcare provider. The initial dose is 140 mg every 2 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose of 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly. Patients should follow the instructions on the prescription label and use the medication exactly as directed by their healthcare provider.
Important Safety Information:
• Repatha may cause serious allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, which are potentially life-threatening. Patients should seek emergency medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, or severe itching or skin rash.
• The medication may also cause injection site reactions, such as redness, swelling, or itching. Patients should consult their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms while taking Repatha.
• Repatha may interact with other medications, and patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including supplements and herbal remedies.
• The medication may increase the risk of developing neurocognitive adverse events, such as memory loss, confusion, or decreased attention span. Patients should discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
Indications:
• Repatha is indicated for the treatment of adults with primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia to reduce LDL cholesterol levels, and in individuals with clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional LDL cholesterol reduction.
Precautions:
• Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to evolocumab or any of its components should not take Repatha.
• The medication should be used with caution in patients with hepatic and renal impairment.
Interactions:
• Repatha may interact with other medications, such as warfarin, and increase the risk of bleeding.
• Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including supplements and herbal remedies, before starting treatment with Repatha.
Contraindications:
• Repatha is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to evolocumab or any of its components.
Overdose:
In case of an overdose, patients should seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Side Effects:
The most common side effects of Repatha include injection site reactions, such as redness, swelling, or itching. Other possible side effects may include upper respiratory tract infections, back pain, and flu-like symptoms. Patients should notify their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms while taking Repatha.
In conclusion, Repatha is a subcutaneous injection used to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in adults with primary hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia and in individuals with clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional LDL cholesterol reduction. It works by binding to and inhibiting proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), promoting the clearance of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Patients should follow the instructions on the prescription label and use the medication exactly as directed by their healthcare provider. Repatha may cause serious allergic reactions and injection site reactions, and patients with a history of hypersensitivity or allergies should not take the medication. The medication should be stored in the refrigerator, and patients should avoid using it if it has been left out of the refrigerator for more than 24 hours.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.