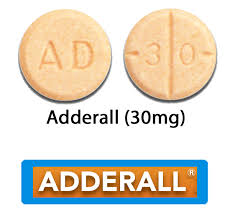
The pill with AD 30 imprinted is orange, round and has been identified as Adderall 30 mg.
It is provided by Shire US Inc.
Description: Adderall is a prescription medication composed of mixed amphetamine salts, including both dextroamphetamine and amphetamine. This combination belongs to a class of drugs known as central nervous system stimulants. Adderall is commonly prescribed to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. The tablet imprinted with “AD 30” is identified as Adderall 30 mg, which signifies the highest dosage strength available in this medication range.
Indications:
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Adderall is prescribed to improve focus, attention span, and impulse control in individuals diagnosed with ADHD. It helps enhance the ability to concentrate, stay focused on tasks, and reduce hyperactive and impulsive behaviors.
- Narcolepsy: Adderall is also used to treat narcolepsy, a condition characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks. It helps patients stay awake during the day.
Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of Action: Adderall works by increasing the levels of neurotransmitters, specifically dopamine and norepinephrine, in the brain. These neurotransmitters play key roles in attention and alertness. By enhancing their activity, Adderall helps improve focus, attention, and wakefulness in individuals with ADHD and narcolepsy.
Dosage and Administration:
- ADHD: The recommended starting dose for children aged 6-17 is 10 mg per day, which may be increased by 10 mg increments at weekly intervals. The maximum recommended dose is 30 mg per day. For adults, the initial dose is typically 20 mg per day.
- Narcolepsy: The usual starting dose for narcolepsy is 10 mg per day for children aged 6-12 and 10 mg per day for adults, with possible increments of 10 mg at weekly intervals. The maximum recommended dose is 60 mg per day.
Adderall is typically taken in the morning to avoid insomnia. It can be taken with or without food, and the tablets should be swallowed whole, not crushed or chewed, to avoid a rapid release of the medication that could increase side effects.
Contraindications:
- Known hypersensitivity or allergic reactions to amphetamine products or any component of Adderall.
- Patients with advanced arteriosclerosis, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, moderate to severe hypertension, hyperthyroidism, or agitated states.
- History of drug abuse or known addiction to stimulants.
- Concurrent use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of stopping MAOI treatment due to the risk of hypertensive crisis.
Warnings and Precautions:
- Cardiovascular Risks: Adderall can cause sudden death in patients with pre-existing structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. It is important to evaluate cardiovascular status before initiating treatment.
- Mental Health: Use with caution in patients with a history of mental health disorders, including bipolar disorder, depression, or psychosis. Stimulants can exacerbate these conditions.
- Growth Suppression: Long-term use of Adderall in children may affect growth rate. Regular monitoring of height and weight is recommended.
- Peripheral Vasculopathy: Stimulants are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Symptoms include numbness, coolness, and color change in fingers or toes.
Adverse Effects: Common side effects of Adderall include:
- Nervousness, restlessness, and anxiety.
- Insomnia or trouble sleeping.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Dry mouth.
- Stomach pain and nausea.
- Headache and dizziness.
Less common but more serious side effects include:
- Cardiovascular issues such as increased heart rate, palpitations, and hypertension.
- Mental health effects such as new or worsening psychosis, mania, or aggression.
- Circulation problems in fingers and toes.
- Seizures in patients with a history of seizures.
Drug Interactions: Adderall can interact with several other medications, potentially altering their effects or increasing the risk of adverse reactions. Notable interactions include:
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Concurrent use with MAOIs can lead to hypertensive crisis.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): May increase the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Antihypertensive Medications: Adderall can reduce the effectiveness of blood pressure medications.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Can affect the absorption and efficacy of Adderall.
Special Populations:
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Adderall is classified as a Pregnancy Category C drug. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Amphetamines are excreted in human milk, and breastfeeding while taking Adderall is not recommended.
- Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of Adderall have not included sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Use caution when prescribing to elderly patients due to the increased risk of cardiovascular and central nervous system side effects.
Storage: Store Adderall at room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from light and moisture. Keep out of reach of children and pets.
Regulatory Status: Adderall is a Schedule II controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act due to its high potential for abuse and dependence. Prescriptions must be written and cannot be refilled; a new prescription is required for each dispensation.
Patient Counseling Information: Patients should be advised on the proper use of Adderall, including the potential for abuse and dependence. It is important to take the medication exactly as prescribed and not to share it with others. Patients should report any cardiovascular symptoms, new or worsening mental health issues, or signs of peripheral vasculopathy to their healthcare provider promptly.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.